Improving home safety in older homes requires a systematic approach to identifying and addressing electrical problems. Many older houses feature outdated wiring and inadequate systems that can create significant hazards. Regular inspections can reveal issues like non-grounded outlets and overloaded circuits. Understanding the risks associated with these common problems is essential. Solutions exist, but knowing when to seek professional assistance is equally important. What steps should homeowners take to guarantee their safety?
Key Takeaways
- Schedule regular electrical inspections to identify outdated wiring and safety hazards in older homes.
- Upgrade circuit panels to handle increased electrical loads safely.
- Install GFCIs in areas prone to moisture to prevent electric shocks.
- Replace outdated two-prong outlets with tamper-resistant models for improved safety.
- Consult a licensed electrician for persistent issues or planned renovations involving electrical systems.
Understanding the Importance of Electrical Safety in Older Homes
While many homeowners appreciate the charm and character of older homes, understanding the importance of electrical safety in these structures is crucial. Aging electrical systems often fall short of modern safety standards, posing potential hazards. Common electrical problems in older homes include outdated wiring, inadequate circuit capacity, and the use of non-grounded outlets. These issues can lead to electrical fires, equipment damage, and personal injury. Additionally, older homes may not have sufficient grounding or protective devices, increasing vulnerability to surges and shorts. Homeowners must recognize these risks and prioritize electrical safety improvements. Engaging qualified professionals for inspections and upgrades guarantees a safer living environment, preserving the home’s character while enhancing its safety for current and future occupants.
Identifying Common Electrical Problems in Older Homes
Identifying common electrical problems in older homes is essential for maintaining safety and functionality. Homeowners should be vigilant for signs such as frequent circuit breaker trips, flickering lights, and outdated two-prong outlets, which indicate potential electrical issues. Additionally, the presence of frayed wires, loose connections, or outdated fuse boxes can compromise safety. It is important to inspect for insufficient grounding and overloaded circuits, as these can lead to hazardous conditions. Homeowners may also encounter outdated electrical panels that cannot handle modern power demands. Conducting regular inspections and enlisting qualified professionals for evaluations can help identify these common electrical issue in older homes, ensuring a safer living environment and enhancing overall home safety.

Dangers of Outdated Wiring and Electrical Systems
Outdated wiring and electrical systems pose significant hazards in older homes, as they often fail to meet current safety standards and electrical demands. Common electrical problems in older homes include deteriorating insulation, which increases the risk of short circuits, and inadequate grounding, leading to potential electric shocks. Additionally, older circuit breakers may not trip during overloads, resulting in fire hazards. The use of obsolete materials, such as aluminum wiring, further exacerbates these dangers due to their tendency to corrode. In addition, insufficient outlets can lead to overextension of extension cords, increasing fire risks. Homeowners should recognize these critical issues to guarantee safety and prevent severe consequences associated with outdated systems, thereby fostering a secure living environment for families.
Solutions for Common Electrical Problems in Older Homes
Addressing common electrical problems in older homes requires a systematic approach to guarantee safety and compliance with modern standards. First, homeowners should conduct a thorough electrical inspection to identify outdated wiring, ungrounded outlets, or inadequate circuit capacity. Upgrading the electrical panel is essential for accommodating increased loads and ensuring ideal performance. Installing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in moisture-prone areas, such as kitchens and bathrooms, enhances safety by preventing electrical shock. Additionally, replacing old outlets with tamper-resistant models can protect against accidental contact. Finally, implementing surge protection devices safeguards sensitive electronics from power surges. By systematically addressing these common electrical issues in older homes, homeowners can markedly enhance safety and functionality within their living spaces.
When to Call a Professional Electrician for Safety Concerns
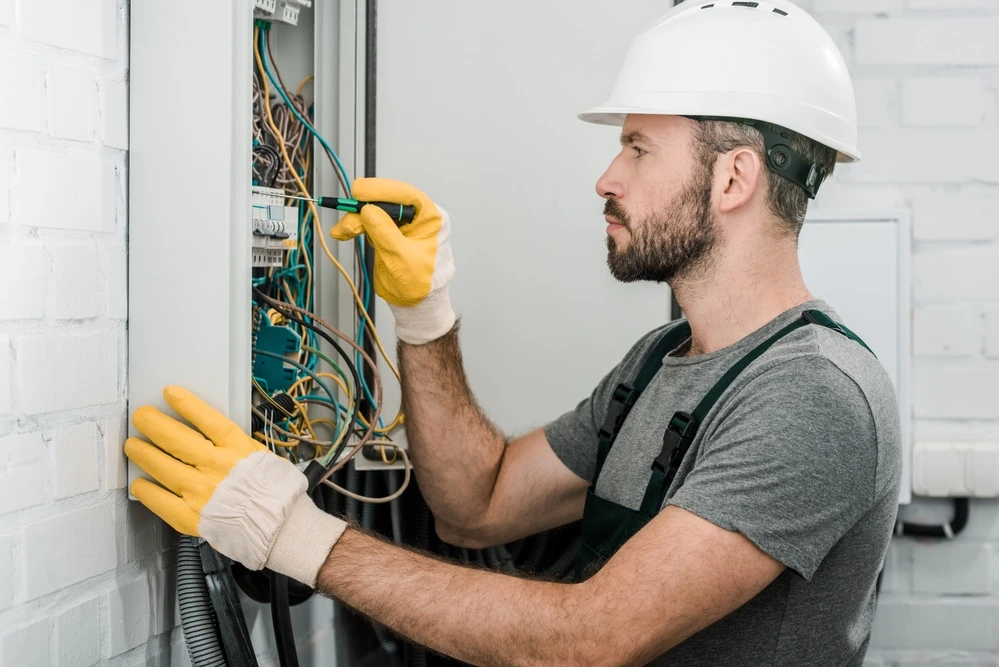
When should homeowners consider enlisting the expertise of a professional electrician for safety concerns? Homeowners should seek professional assistance when encountering persistent electrical issues such as frequent circuit breaker trips, flickering lights, or burning smells emanating from outlets. Additionally, if older homes exhibit outdated wiring systems, such as knob-and-tube or aluminum wiring, a licensed electrician should be consulted to guarantee compliance with current safety standards. Homeowners should also reach out to professionals when planning renovations that involve electrical upgrades or additions. Moreover, any signs of electrical shock when using outlets or appliances indicate immediate professional intervention is necessary. Addressing these common electrical problems in older homes with a qualified electrician promotes safety, enhances property value, and fosters peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Test My Home’s Electrical Safety?
To test a home’s electrical safety, one should inspect outlets for damage, check circuit breakers for tripping, use a multimeter to measure voltage, and consider hiring a licensed electrician for thorough evaluations and necessary repairs.
What Are Signs of Overloaded Circuits?
Signs of overloaded circuits include frequently tripped breakers, flickering lights, warm or discolored outlets, and the smell of burning plastic. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for maintaining electrical safety and preventing potential fire hazards.
Can I Fix Electrical Problems Myself?
It is possible for individuals to fix minor electrical problems themselves, provided they possess the necessary knowledge and skills. However, for complex issues, consulting a licensed electrician is advisable to guarantee safety and compliance with regulations.
What Should I Do During a Power Outage?
During a power outage, individuals should turn off appliances to prevent surges, use flashlights instead of candles for safety, avoid opening refrigerators frequently, and stay updated via battery-operated devices for information on restoration efforts.
How Often Should I Have My Electrical System Inspected?
Electrical systems should be inspected every three to five years, or sooner if issues arise. Regular inspections help identify potential hazards, ensuring safety and efficiency while maintaining the integrity of older home electrical systems.
Conclusion
In summary, enhancing electrical safety in older homes is vital for preventing hazards associated with outdated systems. Regular inspections can identify and mitigate risks such as inadequate wiring and non-grounded outlets. Implementing solutions like GFCIs, surge protection, and tamper-resistant outlets greatly improves safety. Homeowners should prioritize these upgrades and remain vigilant for signs of electrical issues, promptly engaging professional electricians when necessary to guarantee a secure living environment for all residents.
May You Also Like To Read: